Sustainable energy sources are commonly understood as energy sources that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In the past, we have transitioned our major energy sources from Coal to Oil and Gas, which was considered more environment friendly at that time. Now, we are urgently transitioning from Oil and Gas to more greener and sustainable energy sources.
Renewable energy sources are often termed as sustainable energy sources. However, are they truly sustainable? Is the transition sustainable this time around or are we just solving a current problem and creating another one for the future?
Renewable energy is energy from sources that are continuously replenished naturally. Among others, common forms of renewable energy include solar power, wind power, hydroelectric power, tidal power, and biomass energy.
As per the UN Energy Progress Report 2021, the world is making progress towards Goal 7, Affordable and Clean Energy, of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Data from 2018 (latest available) shows that globally the share of renewable energy is 17 per cent of the Total Energy Consumption.
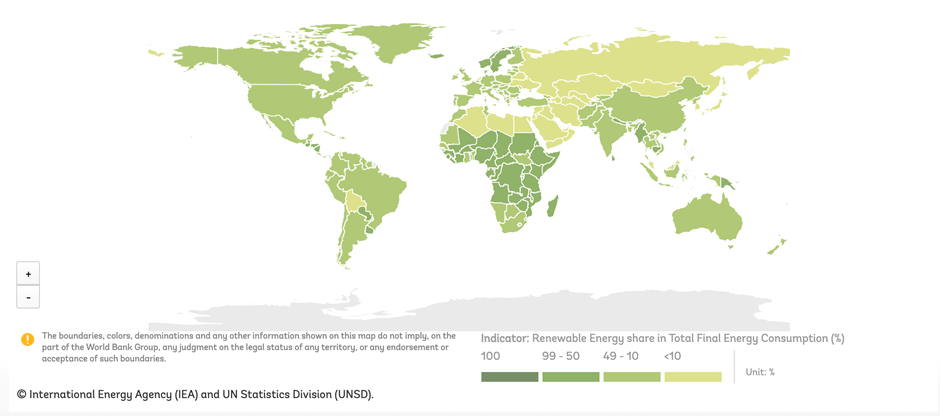
The rapid transition to clean energy is inevitable, but it creates some pertinent questions regarding the Environmental and Social sustainability issues in the transition:
- Environmental sustainability: Let’s not close our eyes for what’s happening. For instance, the mining of Neodymium, a rare earth element important for generator components in wind turbines Mining coal is harmful the environment, but mining neodymium is harmful as well, although considered relatively abundant in the Earth’s crust by some industry experts (opposing views are plenty!)
- Social sustainability: Social aspect is globally diverse and complex. The planet’s resources need to be effectively and efficiently used to provide enough food and energy for everyone. As per the UN Energy Progress Report 2021, 13 per cent of the global population still lacks access to modern electricity and 3 billion people rely on wood, coal, charcoal or animal waste for cooking and heating. Is the transition to renewable energy solving energy poverty globally or is it limited to the fortunate who have had access to energy previously as well?
- ‘True’ sustainability: As renewable energy component of the world’s Total Energy Consumption increase, it brings pressure on the natural resources including water, land use, forestry and marine resources as more resources are required for the renewable infrastructure. Furthermore, indirect impact on biodiversity cannot be ignored. For instance, hydropower or open-cycle power plants involve significant thermal discharges, which could impact the biodiversity. It also raises questions as to whether submerging ecosystems under water by building hydropower dams is less destructive.
Sustainable renewables should be the focus rather than just ‘going green’ by utilising renewable sources, so that the new renewable investments are without the collateral damage and unintended negative consequences. As the pace of transition picks up, and we lay the foundations for a new and sustainable future, it is better to get it right during the transition, than to spend billions correcting the actions decades later.