Integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into investment decision-making have become increasingly popular in recent years. However, the integration has been slow and there are still several challenges associated with effectively integrating ESG factors.
Some of the key challenges faced by investors for ESG integration are:
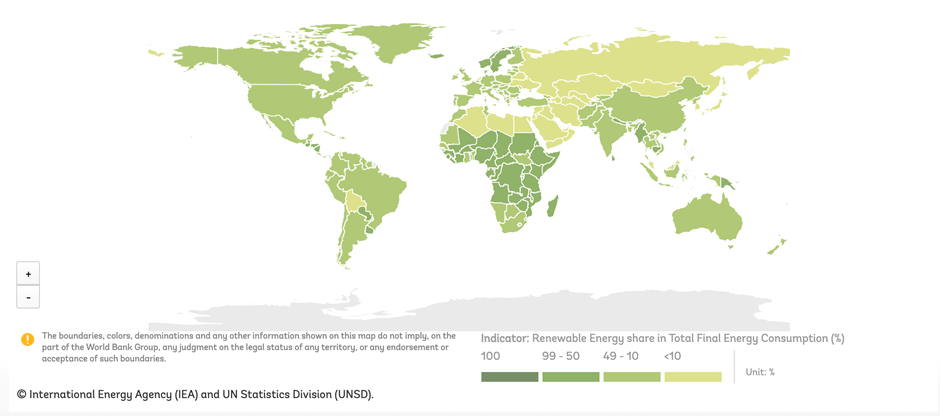
- Lack of standardized ESG data and metrics. ESG data comes from a variety of sources and rating agencies, and as a result, there is often inconsistent information and difficulties in comparing and benchmarking investments. This lack of standardization makes it difficult for investors to assess the materiality of ESG factors in their investment decisions. Additionally, the lack of uniformity in ESG data, definitions, and methodologies presents a major challenge for investors seeking to integrate ESG factors into investment analysis and decision-making. According to the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance’s 2020 Global Sustainable Investment Review, “the lack of uniformity in ESG data, definitions and methodologies presents a major challenge for investors seeking to integrate ESG factors into investment analysis and decision-making.”
- Complexity of ESG issues: The complexity and the need for specialized expertise to fully understand and assess their impact on investments. ESG issues can range from climate change and biodiversity to human rights and labour practices. Understanding these issues requires a deep knowledge of the environmental and social impacts of different industries, as well as an understanding of the regulatory landscape. This complexity can make it difficult for investors to effectively integrate ESG considerations into their decision-making processes. As noted in a report by the Principles for Responsible Investment, “investors may find that ESG analysis requires a greater level of detail and specialized expertise than traditional financial analysis.”
- Reduced financial returns: There is a concern that focusing too much on ESG factors could lead to reduced financial returns. Companies that prioritize ESG issues may face additional costs or have lower profitability in the short term. There is a risk that too much emphasis on ESG factors may come at the expense of financial returns, particularly if investors focus too much on short-term ESG concerns that do not align with long-term financial performance. This concern can make investors hesitant to fully integrate ESG considerations into their decision-making processes.
- ESG considerations with investment objectives: Finally, there is the challenge of balancing ESG considerations with other investment objectives. While ESG factors are important, investors also have other objectives such as achieving financial performance targets or meeting liquidity requirements. Investors must strike a balance between their fiduciary duty to maximize financial returns and their responsibilities to incorporate ESG considerations into their investment processes. As noted in a report by the Principles for Responsible Investment, “investors must also ensure that their investment approach aligns with the objectives and needs of their clients or beneficiaries.”
Addressing concerns:
To address these challenges, a holistic approach is necessary. This approach involves collaboration among different stakeholders, including investors, asset managers, companies, regulators, and standard-setters. The integration of ESG factors into investment analysis and decision-making is a process that requires the involvement of multiple parties, including investors, asset managers, companies, and regulators.
There also needs to be a greater emphasis on developing standardized ESG metrics, improving data quality and availability, and increasing education and training on ESG issues. The Principles for Responsible Investment’s guide on ESG integration for equity investing notes that “investors can improve their ESG integration approach by developing more specific and actionable ESG metrics that are relevant to their investment processes.” Additionally, the guide recommends that investors seek out specialized expertise on ESG issues and invest in training and education for their staff.
Overall, successfully integrating ESG considerations into investment decision-making requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the challenges associated with standardized data, the complexity of ESG issues, financial returns and ESG consideration into investment objectives.